Trump victory big win for Dakota Access Pipeline, but opponents stand strong.
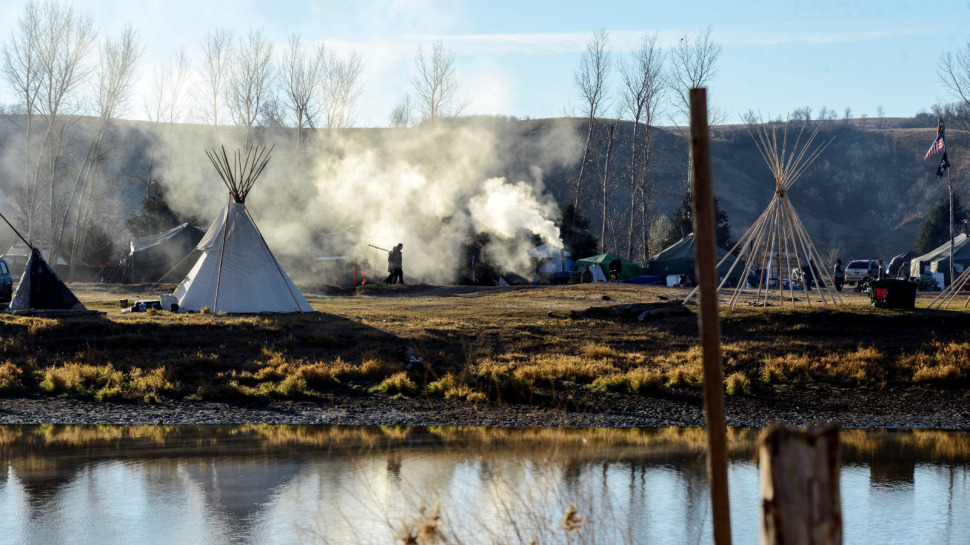

The sound had not been heard in over 150 years. Rising over the remote plains of North Dakota, below a hot November sun and cloudless blue sky, the drums and song of the seven bands of the Sioux nation joined together as tribal elders lit the peta waken (sacred fire) for the first time since Abe Lincoln was President. They were surrounded by some 800 Native Americans and their allies, including women, toddlers, and the elderly, standing silently in a wide circle five people deep, heads bowed in prayer.
“The climate is already at a point of no return,” intoned Lakota Chief Arvol Looking Horse, spiritual leader of the Sioux Nation, from within the circle. “Our waters are polluted by fracking … We must stop this contamination.”
“We are supposed to stop this snake,” Jon Eagle of the Standing Rock Sioux Tribe said in reference to the nearby Dakota Access Pipeline. “We’ve already defeated them; they just don’t know it yet.”
The ceremony was held last weekend to bring renewed unity, grounding, and prayer to the “water protectors,” as they call themselves, gathered together on this windswept grassy field amidst tipis, tents, and morning camp fires at the Oceti Sakowin camp. It is the largest of three makeshift camps erected over the past seven months by the Standing Rock Sioux Tribe and allies near — and at times on top of — the Dakota Access Pipeline route. The 1,200-mile pipeline would carry fracked oil from the Bakken shale regions of North Dakota to Illinois and on to the Gulf Coast, passing half a mile from the Standing Rock Sioux Reservation through areas of tribal spiritual and cultural significance, including under the Missouri River: the primary drinking water source for the tribe and millions of other people downstream.
Barely one week earlier, the water protectors had a pitched battle for territory on which the pipeline was set to pass, including a sacred tribal burial ground. On a hilltop to the north, just behind those gathered for the ceremony, several pieces of bright yellow construction equipment loomed. Dakota Access Pipeline’s operations were actively underway.

Dakota Access Pipeline equipment is seen at the Missouri River near Standing Rock. (Photo: Reuters / Stephanie Keith)
The struggle to stop the pipeline has pitted the water protectors against an increasingly militarized and aggressive police force, with the camps currently under what can only be described as a siege. Floodlights, erected either by Dakota Access or the police (or both), sit atop a hill focused down on Oceti Sakowin, shining all throughout the night, every night. Law enforcement and private security surveillance drones, helicopters, and planes constantly buzz low in circles just overhead.
Highway 1806, leading from the camp to the pipeline and a main artery of rural North Dakota, is blockaded by law enforcement and the burned carcasses of two large trucks. Armored Humvees, often with snipers in their turrets, are a frequent sight. And there is the clear and ever-present danger that if protectors try to get near the pipeline, they will be repelled with extreme measures, including but not limited to: pepper spray, rubber bullets, batons, arrests, and jail. Though these measures have not stopped the protectors — rather, they seem to have strengthened both their numbers and resolve — they have succeeded in facilitating the continued progress of the pipeline construction.
Energy Transfer Partners, the company building the pipeline, said on Thursday that 84 percent of the entire project is complete. It has excavated and is laying pipe nearly up to, and on both sides of, the Missouri River, where just one area remains untouched: that which passes under the river.
![]()
In September, the Obama administration denied Energy Transfer Partners the easement it needs to build under the Missouri River in order to give the Army Corp of Engineers time to review the safety and advisability of doing so. The administration asked that during that review, the company voluntarily pause all construction activity within 20 miles east or west of the river.
The company flatly refused.
On Nov. 4 and again on Thursday, the Army Corps asked Energy Transfer Partners to voluntarily stop work “for a 30-day period to allow for de-escalation,” citing concern “for the safety of all the people involved with the continued demonstrations.” Each time, Energy Transfer Partners refused.
On Sunday, the Norwegian bank DNB, which represents 10 percent of the financing required to build the pipeline, announced that it would consider pulling its support if concerns raised by the Native Americans were not addressed.
Energy Transfer Partners kept building.
Two days later, Citibank, representing 20 percent of the financing, released a statement citing its own “commitment to sustainability and respect for human rights” and advocating for “constructive engagement with the Standing Rock Sioux Tribe in an effort to come to a resolution.”
Dakota Access not only kept building, but released its own statement on Election Day. “To be clear, Dakota Access Pipeline has not voluntarily agreed to halt construction of the pipeline in North Dakota,” it said. Rather, it would be moving horizontal drilling equipment into place in preparation for tunneling under the Missouri River, expecting “no significant delays in its plans to drill under the lake.”
In an interview last week, President Obama said that the Army Corps of Engineers was exploring ways to “reroute” the pipeline around Native American lands.
Asked about Obama’s comments, pipeline spokesperson Vicki Granado told the Guardian: “We are not aware that any consideration is being given to a reroute, and we remain confident we will receive our easement in a timely fashion.”
![]()
Donald Trump was elected president of the United States on Tuesday. The next day, the stock value of Energy Transfer Partners’ parent company rose by 15 percent, as “investors now expect the pipeline to proceed,” Barron’s reported.
“I do expect Trump to approve it,” said Ron Ness, head of the North Dakota Petroleum Council, an industry trade group.
“Dakota Access went from being in some doubt to being a solid bet with this election,” Ethan Bellamy, a senior financial analyst, said.
Much of this confidence is on solid footing.
Trump has between $500,000 and $1 million personally invested in Energy Transfer Partners, with a further $500,000 to $1 million holding in Phillips 66, which will have a 25 percent stake in the Dakota Access project once completed.
Kelcy Warren, chief executive of Energy Transfer Partners, donated $103,000 to elect Trump and $66,800 to the Republican National Committee since Trump became the party nominee.
Many of Trump’s campaign advisors and likely cabinet, moreover, are drawn directly from the ranks of companies involved and invested in the pipeline and in Bakken oil development. Together, they will form one of America’s most fossil-fuel-centric administrations since Warren B. Harding; perhaps even more so than that of George W. Bush. There are fossil fuel company executives, investors, rabid industry cheerleaders, and notorious climate change deniers. Trump has pledged to dramatically increase fossil fuel production from every nook and cranny of the United States, particularly the Bakken shale region.
“Fracking king” Harold Hamm, CEO of Continental Resources, was Trump’s campaign energy advisor and has long been seen as a leading candidate for energy secretary. Continental Resources’ Bakken oil will be carried via the completed Dakota Access Pipeline, according to its November update to investors.
Trump campaign advisor John Paulson — president and CEO of Paulson & Co. and “one of the titans of the U.S. hedge fund industry,” managing some $14 billion — is heavily invested in the U.S. oil and gas industry, particularly in the Bakken. After becoming the largest shareholder in Whiting Petroleum in 2013, Paulson surpassed Hamm to become the largest producer of oil in North Dakota before selling off his entire Whiting holdings earlier this year. Paulson’s continued investments in the sector include Oasis Petroleum, renowned for its role in the single worst accident in Bakken history, involving a blowout, explosion, two worker deaths, and a worker suicide.
Oasis is working to complete a 19-mile oil transmission system from its North Dakota petroleum handling facility to the Dakota Access Pipeline, thus positioning it to supply roughly one-ninth of the pipeline’s estimated 470,000 barrels of daily crude oil deliveries, records from the North Dakota Public Service Commission show.

The Dakota Access Pipeline is seen near New Salem, North Dakota. (Photo: Tony Webster)
According to Oasis Petroleum’s most recent financial filings, Paulson’s hedge fund owns the fourth-largest share of the company. Trump has invested between $3 million and $15 million in Paulson’s hedge funds.
Dennis Nuss of Phillips 66, a 25 percent owner of the Dakota Access Pipeline, said Wednesday that the pipeline should be fully operational in the first quarter of 2017.
Doing so, however, would require that the Army Corps of Engineers grant the easement, either under the Obama or Trump administrations.
![]()
Last week, Standing Rock Sioux Chair Dave Archambault II recommitted the tribe to the fight against the pipeline. “If there is an easement granted,” he said, “we will sue.”
The tribe has a federal lawsuit against the Army Corps of Engineers pending, which argues that the Corps failed to adequately consult with the tribe and that granting the easement for the pipeline to pass under the Missouri River would do irreparable harm.
U.S. District Judge James Boasberg rejected these arguments on Sept. 9, but only under the National Historic Preservation Act. The underlying lawsuit also argues that the Corps’ permitting process violated the Clean Water Act, the National Environmental Policy Act, and the Rivers and Harbors Act. None of those claims has been fully litigated.
Another lawsuit underway in Iowa goes to court next month. Landowners in six counties there argue that Energy Transfer Partners’ claims of eminent domain when using their land for the pipeline were unlawful.
Protests have also been ongoing in the state, continuing on Thursday, when three protectors — bearing food, water, and sleeping bags — locked themselves inside of the pipeline. They halted construction for 17 hours next to a sign reading: “No Eminent Domain for Private Gain.”
![]()
President Obama has 70 days left in office before Donald Trump is sworn in on Jan. 20. Late Friday, conflicting reports from the administration were reported by Politico and Reuters, originally suggesting that the Obama administration might go ahead and give its approval to the pipeline on Monday, then denying those reports, then quoting spokesperson Amy Gaskill of the U.S. Army Corps of Engineers that a decision “would come in the next few days, possibly by Monday.”
Lorrena Alameda, age 33, and her mother Gladys Renville, age 55, Dakota Sioux from South Dakota, are among the thousands of people from some 200 tribes who have flocked to Standing Rock to defend the water and the land, including some 6,000 people this past weekend alone. Alameda expects President Obama to take action on their behalf.
“I feel like all the promises he made to us, he needs to be there right now and tell [Energy Transfer Partners] to stop doing what they’re doing, and he needs to enforce it,” Alameda tells me. “Because, right now, everything that happens here is on his watch.”
Obama has many options. He can deny the easement and order the Army Corps of Engineers to conduct a full Environmental Impact Statement (EIS). This was not done, the Sierra Club’s Catherine Collentine explains, because the pipeline was “fast-tracked” using a far less comprehensive environmental assessment.
The administration could deny the easement and remain open to the pipeline crossing the Missouri River at another location — i.e. reroute the pipeline. Regardless of whether the reroute also requires an EIS, it would by definition require additional study by both the federal government and the company — all of which would be both time-consuming and costly.
Every day the project is stalled or incomplete costs money, adds more time for action by the protectors and their allies, and builds concern among investors.
Energy Transfer Partners is already suffering financially, reporting on Thursday a whopping 82 percent collapse in profits in the third quarter of 2016 versus the same period last year. Moreover, it originally committed to completing the pipeline by Jan. 1, but now predicts that it will not be operational until April. Every day the Jan. 1 deadline is not met, shippers planning on using it can terminate their contracts.
Finally, Obama can deny this, or any other easement for crossing the Missouri, thereby killing the Dakota Access Pipeline altogether.
In the midst of the historic peta waken ceremony, a tribal elder admonished the President, saying, “Obama, he started this, saying what our children can be. I say, ‘Don’t start it if you can’t finish it!’ I learned that in Cambodia.”
Any of these decisions could be undone or reversed by the incoming Trump administration. But doing so would also open the door to further litigation, something Jan Hasselman of Earthjustice, the attorney representing the Standing Rock Sioux, says he is fully prepared to do. If Obama grants the easement, that too can be litigated.
![]()
Those at Standing Rock remain unflinching in their commitment to stop the pipeline. Most could not be reached for comment on Friday as they were busy stopping work on the pipeline for several hours by blocking the pipeline route and taking over Dakota Access construction equipment near Highway 6; while others were busy winterizing the camps.
Their Facebook pages are replete with responses to Trump’s election, however, including this oft-posted image. “Disappointed, but not surprised” is a common theme, as is a renewed hope that President Obama will take swift action while still in office and that support from allies will grow, such as the protests at banks that invest in the project and the “Stand for Standing Rock” day of action on Nov. 15 at Army Corps of Engineers offices around the country.
Stopping the project is the option most favored by those at Standing Rock as they do not wish the problems they seek to avoid near their home thrust upon others. Most also seek to end dependence on oil altogether.
Chair Archambault declared as the fire ceremony drew to a close: “We have to decrease the dependency on how we use oil. If not, this is just one pipeline. There will be more.”

